Recently, there have been reports of a new virus outbreak in China and various parts of the world. This virus is known as Human Metapneumovirus (HMPV). Due to recent outbreaks in regions such as China and India, there is growing panic among many people, as the number of cases continues to rise. Let us learn more about Human Metapneumovirus (HMPV)—how it is transmitted, what are its symptoms, and how it can be treated.
What Is Human Metapneumovirus (HMPV)?
Human Metapneumovirus (HMPV) is a respiratory pathogen that has garnered attention due to recent outbreaks in various regions, including China and India. First discovered in 2001, HMPV is a member of the Paramyxoviridae family, closely related to the Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV). The respiratory system is primarily impacted, leading to mild to severe infections across a range of age groups. Although the majority of infections are minor and resolve on their own, some groups are more vulnerable to consequences, including small children, the elderly, and people with weakened immune systems. This article explores the symptoms, transmission, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention strategies for HMPV.
Symptoms Of HMPV (Human Metapneumovirus)

HMPV infections present symptoms similar to the common cold, but they can escalate depending on the individual’s immune response and underlying health conditions. People infected with HMPV may experience fever, cough, a runny or stuffy nose, and a sore throat. Wheezing and shortness of breath are also common, and some individuals may develop a rash. In severe cases, HMPV can lead to lower respiratory tract infections such as bronchiolitis, pneumonia, and exacerbation of chronic respiratory diseases like asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Infants, especially those between 6 and 12 months and older adults above 65, are more prone to complications.
How Does HMPV Spread?
HMPV is highly contagious and primarily spreads through respiratory droplets generated by coughing or sneezing. The virus can also spread through contact with contaminated surfaces, such as door handles, phones, or toys, and by direct physical contact, such as shaking hands or hugging an infected person. This virus is most prevalent during winter and early spring. It is estimated to account for 10% to 12% of respiratory illnesses in children, with some cases progressing to severe complications.
Risk Factors And Vulnerable Groups
Certain individuals face a higher risk of severe illness from HMPV. Children under five years old, particularly infants and premature babies, are more vulnerable. Similarly, older adults over 65 years of age are at a higher risk due to weaker immunity. Individuals with weakened immune systems—caused by conditions like HIV, cancer, or autoimmune diseases or due to medications that suppress immunity—are also more susceptible. Those with chronic respiratory issues, such as asthma or COPD, may experience worsened symptoms when infected.
Diagnosis And Testing For HMPV
Healthcare providers diagnose HMPV based on clinical symptoms and medical history. In severe cases, they use diagnostic tools such as nasal or throat swabs to collect samples that are sent to laboratories to detect the virus. In complicated cases, bronchoscopy or chest X-rays may be used to identify changes in the lungs. Routine testing for HMPV is rare unless symptoms are severe or the patient belongs to a high-risk group.
HMPV Treatment
There are no particular antiviral drugs available at this time to treat HMPV. The main goals of treatment are symptom management and supportive care. In mild cases, people can take over-the-counter drugs such as cough suppressants, pain relievers, and decongestants to reduce symptoms. They are also urged to stay hydrated by drinking lots of fluids. Recovery also requires getting enough sleep. Hospitalization may be necessary in severe cases, where corticosteroids are used to reduce inflammation and alleviate symptoms, intravenous fluids are used to maintain hydration, and oxygen therapy is used to help with breathing. Since HMPV is a viral illness, antibiotics are ineffective against it. However, antibiotics might be recommended to treat a subsequent bacterial infection if one arises.
How To Prevent HMPV Infections?
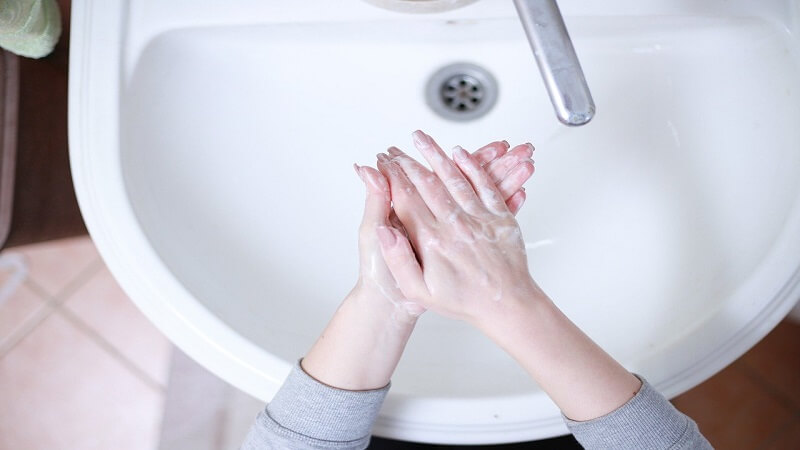

To stop HMPV from spreading, preventive steps are essential. It’s important to regularly wash your hands with soap and water for at least 20 seconds. If soap isn’t available, you can use alcohol-based hand sanitizers. The distribution of droplets can be reduced by covering the mouth and nose when sneezing or coughing, ideally with an elbow or tissue. Wearing masks in crowded or high-risk settings and avoiding close contact with ill people can help lower the risk even more. Regular disinfection is also necessary for frequently touched surfaces, such as cell phones and doorknobs. Avoid sharing cups, utensils, or food with other people as well, especially in homes with elderly people, children, or those with long-term medical conditions.
Outlook And Prognosis
HMPV infections usually go away in a week for most people who get enough sleep and drink plenty of water. Coughing and exhaustion, for example, may persist for a longer period. Intense care may be necessary for severe instances, especially in high-risk groups, and recovery times may be prolonged. If symptoms develop or consequences like breathing difficulties, blue skin, or a persistently high temperature appear, you must get medical help. Results can be greatly enhanced by prompt intervention, particularly for those who are more susceptible.
Final Thoughts
Human Metapneumovirus is a common yet potentially serious respiratory virus. Understanding its symptoms, transmission, and preventive actions is essential, especially for those who are more susceptible to problems, even if the majority of cases are mild. Better health outcomes for everyone can be ensured by reducing the spread of HMPV through public knowledge and commitment to preventive measures. For an accurate diagnosis and course of treatment, see a healthcare professional if you or a loved one experience respiratory symptoms that worsen or last longer. To safeguard people who are most susceptible to serious illness, early care and intervention are crucial.
Follow Us: Facebook | Instagram | X |
Youtube | Pinterest | Google News |
Entertales is on YouTube; click here to subscribe for the latest videos and updates.